OpenAI New AI Tool to Check Content Authenticity
Updated: May 07 2024 22:35As generative AI continues to revolutionize the way we create and consume digital content, the need for robust content authentication measures has never been more pressing. With the rise of tools like DALL·E 3, which enable users to generate and edit images, videos, and audio with unprecedented ease, it is crucial to develop standards and technologies that help people understand the origins of the content they encounter online. This is
OpenAI's two-pronged approach to addressing this challenge by contributing to the development of open standards for content provenance and creating new tools to identify content generated by OpenAI services.
OpenAI Joins the C2PA Steering Committee
OpenAI recognizes the importance of establishing common methods for sharing information about the creation of digital content. To this end, OpenAI have joined the Steering Committee of the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA), a widely adopted standard for digital content certification. By contributing to the development of C2PA, OpenAI aim to promote transparency and trust in the digital content ecosystem.
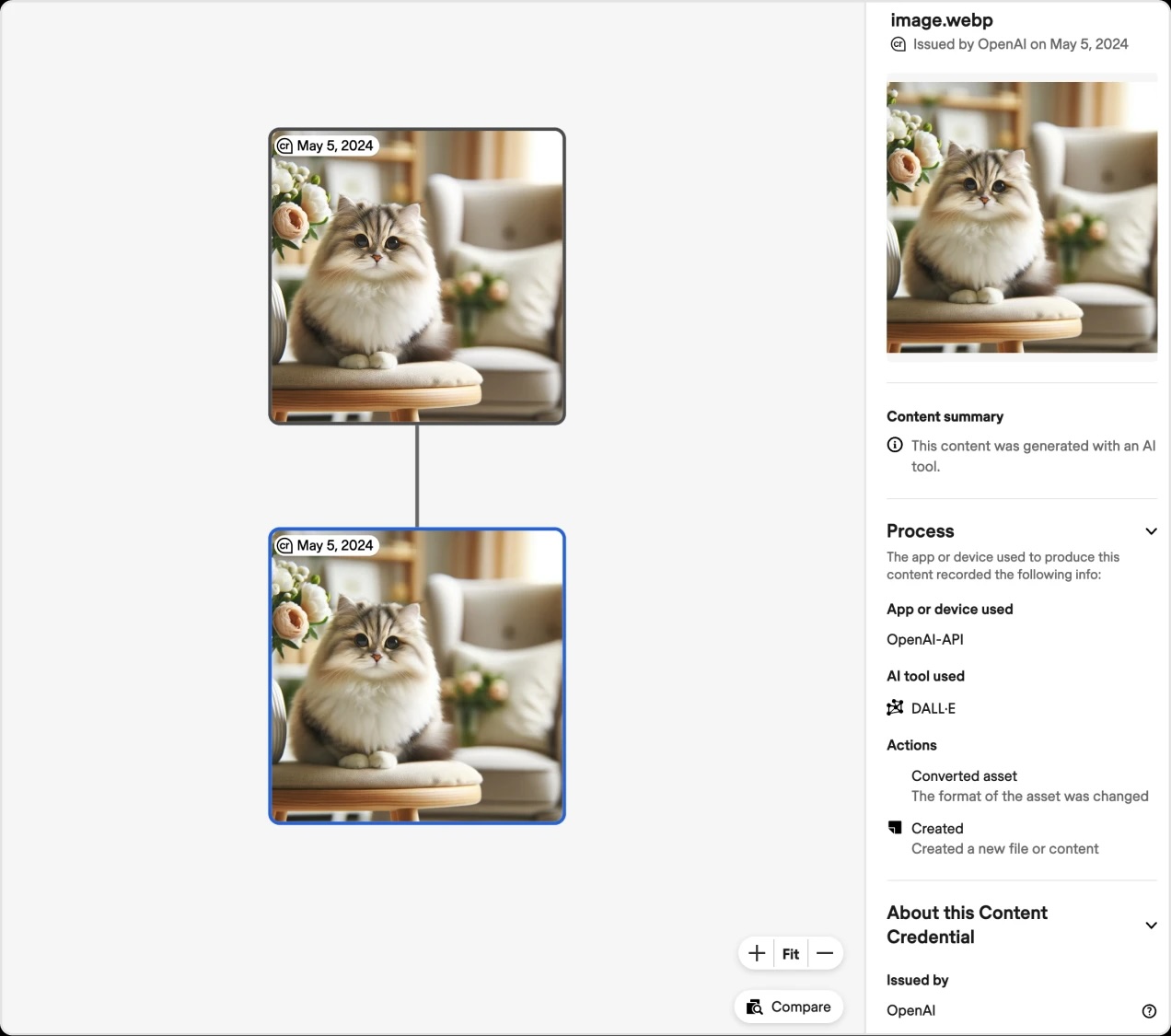
Starting with DALL·E 3, OpenAI have begun adding C2PA metadata to all images created and edited using its tools, both in ChatGPT and the OpenAI API. This metadata provides valuable information about the content's origins, making it easier for users to verify the authenticity of the images they encounter. As OpenAI prepare to launch Sora, it will also integrate C2PA metadata to ensure that the commitment to content authenticity extends across all our generative AI offerings.
While bad actors may still attempt to create deceptive content or remove the C2PA metadata, this information serves as an important resource for building trust. As the adoption of C2PA increases, OpenAI believe that this metadata will become an expected feature, filling a critical gap in digital content authenticity practices.
The OpenAI and Microsoft Fund
To further drive the adoption and understanding of provenance standards like C2PA, OpenAI has partnered with Microsoft to launch a $2 million societal resilience fund. This fund will support AI education and understanding through organizations such as Older Adults Technology Services from AARP, International IDEA, and Partnership on AI. By investing in these initiatives, OpenAI aim to foster a more informed and resilient society in the face of rapidly evolving AI technologies.
Tamper-Resistant Watermarking and Detection Classifiers
In addition to the support for C2PA, OpenAI is actively developing new provenance methods to enhance the integrity of digital content. These include tamper-resistant watermarking, which invisibly marks digital content like audio with a signal that is difficult to remove, and detection classifiers, which use AI to assess the likelihood that content originated from generative models.
OpenAI is opening applications for access to OpenAI's image detection classifier through the Researcher Access Program. This tool, designed to predict the likelihood that an image was generated by DALL·E 3, will be available to research labs and research-oriented journalism nonprofits for feedback and analysis. By enabling independent research on the classifier's effectiveness, real-world applications, and the characteristics of AI-generated content, OpenAI hope to gain valuable insights that will inform our ongoing efforts to promote content authenticity.
Internal testing has shown that this classifier achieves high accuracy in distinguishing between non-AI generated images and those created by DALL·E 3. OpenAI are committed to ongoing research and development to refine the detection classifiers and ensure their reliability across a wide range of scenarios.
Google Takes a Stand Against Deepfake Pornography by Banning Ads
In a move to combat the growing concern of deepfake pornography, Google has announced a ban on ads for platforms that generate this type of content. Starting May 30, websites and apps that enable users to create realistic artificial pornography will no longer be allowed to place ads through Google's extensive advertising network. This ban also extends to platforms that promote, compare, or provide instructions on creating deepfake pornography.
Google's decision to ban ads for deepfake pornography platforms is a crucial step in the right direction. As one of the world's largest tech companies, Google has a significant influence on the digital landscape. By cutting off a major revenue stream for these platforms, Google is sending a clear message that it will not tolerate or support the creation and dissemination of non-consensual pornographic content.
The
updated Inappropriate Content Policy, which came into effect on May 1, demonstrates Google's commitment to maintaining a safe and ethical advertising ecosystem. The policy has long prohibited marketing content that promotes violence, self-harm, hate groups, or exploits shocking imagery for attention.
Collaboration and Collective Action
Transparency and research are also key priorities for OpenAI. The company is actively seeking feedback on its content identification tools through the Researcher Access Program, which grants access to the image detection classifier for research purposes. This allows independent evaluation of the tool's effectiveness and further exploration of AI-generated content characteristics.
While OpenAI's initiatives represent significant steps towards a more transparent online world, the journey towards robust content authentication is ongoing. Collaboration within the industry, advancements in technology, and user education will all play crucial roles in ensuring a future where trust and authenticity prevail in the digital realm.
Google's ban on ads for deepfake pornography platforms is a necessary and timely move. As technology continues to advance, it is crucial for tech giants to take proactive measures to prevent the misuse of their platforms and services. Microsoft has developed an
authenticator tool about 4 years ago that can analyze photos or videos to give a confidence score on whether it's been manipulated. It certainly needs to be updated with the latest AI technologies.
Intel's
FakeCatcher is another one that uses algorithms to analyze subtle physiological details like blood flow variations in pixels, enabling real-time detection with high accuracy (96%). Similarly, the tool was developed about 4 years ago and seriously need some new updates.
Check out my recent posts